Page 6 - i1052-5173-31-5
P. 6
10 2 Effectively, each datum can be thought of
A SGP B
USGS-CMIBS as a Gaussian distribution along the time axis
USGS-NGDB with a s of at least 25 million years (the
10 1 minimum value of which may be thought of
as a kernel bandwidth, rather than an analyti-
cal uncertainty). The selection of this s value
Sample ID Gap Sample ID Gap 75th cesses that are being investigated (e.g., tec-
10 0 should correspond to an estimate of the pro-
Median tonic changes in provenance). We did not
impose a minimum relative age uncertainty.
10 -1 With respect to measurement uncertainties,
25th
48,234
20,813
20,813 13,531 48,234 we assigned an absolute uncertainty to every
13,531
analyte that lacked one by multiplying the
10 ² reported analyte value by a relative error. In
-
0 2 4 6 8 10 SGP USGS- USGS- future database projects, there is considerable
scope to go beyond this coarse uncertainty
Sample ID x10 Source quantification strategy. For example, given
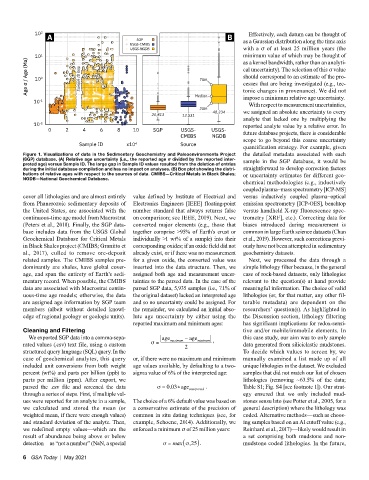
Figure 1. Visualizations of data in the Sedimentary Geochemistry and Paleoenvironments Project the detailed metadata associated with each
(SGP) database. (A) Relative age uncertainty (i.e., the reported age σ divided by the reported inter- sample in the SGP database, it would be
preted age) versus Sample ID. The large gap in Sample ID values resulted from the deletion of entries
during the initial database compilation and has no impact on analyses. (B) Box plot showing the distri- straightforward to develop correction factors
butions of relative ages with respect to the sources of data. CMIBS—Critical Metals in Black Shales; or uncertainty estimates for different geo-
NGDB—National Geochemical Database.
chemical methodologies (e.g., inductively
coupled plasma–mass spectrometry [ICP-MS]
cover all lithologies and are almost entirely value defined by Institute of Electrical and versus inductively coupled plasma–optical
from Phanerozoic sedimentary deposits of Electronics Engineers [IEEE] floating-point emission spectrometry [ICP-OES], benchtop
the United States, are associated with the number standard that always returns false versus handheld X-ray fluorescence spec-
continuous-time age model from Macrostrat on comparison; see IEEE, 2019). Next, we trometry [XRF], etc.). Correcting data for
(Peters et al., 2018). Finally, the SGP data- converted major elements (e.g., those that biases introduced during measurement is
base includes data from the USGS Global together comprise >95% of Earth’s crust or common in large Earth science datasets (Chan
Geochemical Database for Critical Metals individually >1 wt% of a sample) into their et al., 2019). However, such corrections previ-
in Black Shales project (CMIBS; Granitto et corresponding oxides; if an oxide field did not ously have not been attempted in sedimentary
al., 2017), culled to remove ore-deposit already exist, or if there was no measurement geochemistry datasets.
related samples. The CMIBS samples pre- for a given oxide, the converted value was Next, we processed the data through a
dominantly are shales, have global cover- inserted into the data structure. Then, we simple lithology filter because, in the general
age, and span the entirety of Earth’s sedi- assigned both age and measurement uncer- case of rock-based datasets, only lithologies
mentary record. When possible, the CMIBS tainties to the parsed data. In the case of the relevant to the question(s) at hand provide
data are associated with Macrostrat contin- parsed SGP data, 5,935 samples (i.e., 7.1% of meaningful information. The choice of valid
uous-time age models; otherwise, the data the original dataset) lacked an interpreted age lithologies (or, for that matter, any other fil-
are assigned age information by SGP team and so no uncertainty could be assigned. For terable metadata) are dependent on the
members (albeit without detailed knowl- the remainder, we calculated an initial abso- researchers’ question(s). As highlighted in
edge of regional geology or geologic units). lute age uncertainty by either using the the Discussion section, lithology filtering
reported maximum and minimum ages: has significant implications for redox-sensi-
Cleaning and Filtering tive and/or mobile/immobile elements. In
We exported SGP data into a comma-sepa- age − age minimum , this case study, our aim was to only sample
rated values (.csv) text file, using a custom σ= maximum data generated from siliciclastic mudstones.
structured query language (SQL) query. In the 2 To decide which values to screen by, we
case of geochemical analytes, this query or, if there were no maximum and minimum manually examined a list made up of all
included unit conversions from both weight age values available, by defaulting to a two- unique lithologies in the dataset. We excluded
percent (wt%) and parts per billion (ppb) to sigma value of 6% of the interpreted age: samples that did not match our list of chosen
parts per million (ppm). After export, we lithologies (removing ~63.5% of the data;
parsed the .csv file and screened the data σ= 0.03 age interpreted . Table S1; Fig. S4 [see footnote 1]). Our strat-
∗
through a series of steps. First, if multiple val- egy ensured that we only included mud-
ues were reported for an analyte in a sample, The choice of a 6% default value was based on stones sensu lato (see Potter et al., 2005, for a
we calculated and stored the mean (or a conservative estimate of the precision of general description) where the lithology was
weighted mean, if there were enough values) common in situ dating techniques (see, for coded. Alternative methods—such as choos-
and standard deviation of the analyte. Then, example, Schoene, 2014). Additionally, we ing samples based on an Al cutoff value (e.g.,
we redefined empty values—which are the enforced a minimum s of 25 million years: Reinhard et al., 2017)—likely would result in
result of abundance being above or below a set comprising both mudstone and non-
detection—as “not a number” (NaN, a special σ= max σ,25 . mudstone coded lithologies. In the future,
6 GSA Today | May 2021